Ejercicios de SOME y ANY
Finalmente, realizaremos una actividad de comprensión para que medir tu entendimiento del tema.
Usamos _______ para oraciones afirmativas y para preguntas sólo si son OFERTAS (Would you like..?) o SOLICITUDES (Can I have…?)
They have _______ houses.
Vocabulary
Have: Tener
Houses: Casas
She doesn’t want _______ beer.
Vocabulary
Want: Querer
Beer: Cerveza
She doesn’t want _______ beer.
Vocabulary
Want: Querer
Beer: Cerveza
Are there _______ messages for me?
Vocabulary
There are: Hay
Messages: Mensajes
Can I have _______ water, please?
Vocabulary
Can: Poder
Water: Agua
Can I have _______ water, please?
Vocabulary
Can: Poder
Water: Agua
We bought _______ meat.
Vocabulary
Bought: Verbo “comprar” en pasado
Meat: Carne
Can I have _______ more wine, please?
Vocabulary
Can: Poder
Wine: Vino
Do you have _______ questions?
Vocabulary
Have: Tener
Questions: Pregunta
Excuse me, would you like _______ suggar in your coffee?
Vocabulary
Would you like: Le gustaría
Coffee: Café
I did not eat _______ meat.
Vocabulary
Eat: Comer
Meat: Carne
Can I have _______ cake, please?
Vocabulary
Can: Poder
Cake: Bizcocho, pastel o tarta
Do you have _______ friends from Canada?
Finalmente, realizaremos una actividad de comprensión para que medir tu entendimiento del tema.
En este texto, una esposa le deja un mensaje a Mike, su esposo, diciéndole que por favor compre algunas cosas para la casa. Escribe some o any para completar el texto:
- Dear Mike,
We don’t have milk left. Please buy some. We need eggs for Annie’s breakfast. The cat doesn’t have food left, so buy 3 kilos of cat food. Tomorrow, I’m going to make sandwiches for dinner, so we need bread, cheese and 2 tomatoes. We do not need ham because I bought yesterday.
Love, Laura
- Dear Mike,
Elige la opción correcta.
1 There is ____ beer in the fridge.
2 Are there ____ grapes in the kitchen?
3 I've got ____ nice rings and bracelets.
4 There isn't ____ wine in my glass.
5 There aren't ___ lions in Greenland.
6 Has your mother got ____ brothers or sisters?
7 We had ___ snow this evening.
8 I can't eat ____ more meat but I'd like ____ more wine, please.
9 Don't make ____ noise. She wants to get ____ sleep.
10 ____ people are very good with languages.
11 There are vegetables in the oven.
12 Have you got mushrooms?
13 Emma has got old pictures in her house.
14 There aren't buses on Sundays.
15 She never has fun.
16 If you find mistakes, please let me know.
17 He brought me beautiful roses.
18 Is there soup left?
19 Have you got free time next Saturday?
20 I have just made coffee, can I get you a cup?
Articles exercise A, AN, SOME, ANY
Escribe solamente some o any en los espacios.
Ejemplo:
There is ____ beer on the table.
Respuesta:
some
Ejercicios del presente simple negativo I
Presente simple negativo. Elige la opción correcta.
1 He ____ a book every month.
2 You ____ my girlfriend yet.
3 Your grandmother ____ in Chicago.
4 They ____ to the beach on their holiday.
5 He ____ any magazine.
6 Peter and Tom ____ to the gym.
7 My neighbour's dog ____ too loudly.
8 I ____ to understand him.
9 The world population ____ above three billion people a year.
10 My brother ____ pasta.
Ejercicios de SOME y ANY
Finalmente, realizaremos una actividad de comprensión para que medir tu entendimiento del tema.
Usamos _______ para oraciones afirmativas y para preguntas sólo si son OFERTAS (Would you like..?) o SOLICITUDES (Can I have…?)
They have _______ houses.
Vocabulary
Have: Tener
Houses: Casas
She doesn’t want _______ beer.
Vocabulary
Want: Querer
Beer: Cerveza
She doesn’t want _______ beer.
Vocabulary
Want: Querer
Beer: Cerveza
Are there _______ messages for me?
Vocabulary
There are: Hay
Messages: Mensajes
Can I have _______ water, please?
Vocabulary
Can: Poder
Water: Agua
Can I have _______ water, please?
Vocabulary
Can: Poder
Water: Agua
We bought _______ meat.
Vocabulary
Bought: Verbo “comprar” en pasado
Meat: Carne
Can I have _______ more wine, please?
Vocabulary
Can: Poder
Wine: Vino
Do you have _______ questions?
Vocabulary
Have: Tener
Questions: Pregunta
Excuse me, would you like _______ suggar in your coffee?
Vocabulary
Would you like: Le gustaría
Coffee: Café
I did not eat _______ meat.
Vocabulary
Eat: Comer
Meat: Carne
Can I have _______ cake, please?
Vocabulary
Can: Poder
Cake: Bizcocho, pastel o tarta
Do you have _______ friends from Canada?
Finalmente, realizaremos una actividad de comprensión para que medir tu entendimiento del tema.
En este texto, una esposa le deja un mensaje a Mike, su esposo, diciéndole que por favor compre algunas cosas para la casa. Escribe some o any para completar el texto:
- Dear Mike,
We don’t have milk left. Please buy some. We need eggs for Annie’s breakfast. The cat doesn’t have food left, so buy 3 kilos of cat food. Tomorrow, I’m going to make sandwiches for dinner, so we need bread, cheese and 2 tomatoes. We do not need ham because I bought yesterday.
Love, Laura
- Dear Mike,
Ejercicios del presente simple negativo I
Presente simple negativo. Elige la opción correcta.
1 He ____ a book every month.
2 You ____ my girlfriend yet.
3 Your grandmother ____ in Chicago.
4 They ____ to the beach on their holiday.
5 He ____ any magazine.
6 Peter and Tom ____ to the gym.
7 My neighbour's dog ____ too loudly.
8 I ____ to understand him.
9 The world population ____ above three billion people a year.
10 My brother ____ pasta.
- 1) «Some» se utiliza en oraciones afirmativas.
- 2) «Any»: se utiliza en oraciones negativas o interrogativas.
- «Some» se utiliza a veces en preguntas:
- «Any» se utiliza a veces:
“Any” y “some” son las palabras cuantitativas utilizadas con mayor frecuencia en el idioma inglés. Si no sabemos utilizarlas apropiadamente ¡puede partirnos la cabeza! A continuación te explicamos de manera directa lo que significan.
Any / Some
Ambos adjetivos se traducen como «algo de» / «algunos», respectivamente.
Regla general:
1) «Some» se utiliza en oraciones afirmativas.
There are some letters for you.
Hay algunas cartas para ti
There is some sugar in the pot.
Hay algo de azúcar en el recipiente
2) «Any»: se utiliza en oraciones negativas o interrogativas.
We haven´t got any shirts in your size.
No tenemos camisas de su talla
There aren´t any bottles of milk in the fridge.
No hay botellas de leche en el refrigerador.
Have you got any shirts in my size?
¿Tienen algunas camisas de mi talla?
Are the any bottles of milk in the refrigerator?
¿Hay botellas de leche en el refrigerador?
Particularidades:
«Some» se utiliza a veces en preguntas:
1a) Que suponen ofrecimiento:
Do you want…?
Can I give you some advice?
1b) Cuando se espera casi con toda seguridad una respuesta afirmativa.
Can I have some biscuits?
«Any» se utiliza a veces:
1a) En oraciones afirmativas con el significado de «cualquiera».
Any kid would have behaved like that
You can pick any of these books
You can go anywhere you want
1b) En oraciones condicionales con el significado de «alguien, algo, alguna cosa».
If anyone ask for me, please tell them I will be back soon
If anything happens, please call me immediately
If I had any money I would buy a new car
La excepción confirma la regla
Como hemos dicho al principio, en general some se emplea en frases afirmativas y any en frases negativas e interrogativas.
Sin embargo, hay excepciones a esta regla y vamos a aprender una de ellas ahora.
Se puede utilizar some para ofrecer algo.
En este caso esperamos una respuesta afirmativa a nuestra pregunta.
Simplemente es una forma educada para preguntar si alguien desea tomar algo:
Would you like some tea?
(¿Te apatece un té?)
Do you want some biscuits?
(¿Quieres galletas?)
How about some more coffee?
(¿Qué tal más café?)
Complete the sentences with a, an, some or any.
1. Is there water left?
2. I usually have chocolate at night.
3. There isn't pen on the table.
4. There are students in the classroom.
5. There is student in the classroom.
6. There isn't milk in the fridge.
7. Are there books in your schoolbag?
8. She is friend of mine.
9. She is such intelligent girl.
10. There aren't people in that pub.
Escribe solamente some o any o a o an en los espacios.
Ejemplo:
There are ____ serviettes in the cupboard.
Answer:
some
Ejercicios: presentsimple y continuous
Ahora, vamos a practicar un poco con estos ejercicios. Solo tienes que completar las frases propuestas con la forma adecuada de presente simple o continuo del verbo entre paréntesis. Encontrarás las soluciones más abajo pero recuerda, ¡no vale hacer trampas!
1) I _____ (work) for the Government.
2) The sun _____ (set) in the west.
3) The milk _____ (boil) already. Can you turn off the stove?
4) Peter is sick, so he _____ (not work) tomorrow.
5) I _____ to the radio in my way to work every morning.
6) I have a chronic condition, so I _____(take) a pill daily.
7) Who is that girl? Why _____ she _____ (dance) alone?
8) My mother _____ (say) she’s 55, but nobody _____ (believe) her.
9) Where _____ you _____(work)?
10) Listen! They are _____(play) that song you really like.
11) I have cabin fever, I really _____(want) to go outside.
12) My grandparents _____(love) each other so much -it’s very sweet!
13) I _____(stay) at this hostel during my next trip.
14) Please, stay quiet. I_____ (try) to work here!
15) My cousin _____(have) really long hair.
16) I often _____(sing) in the shower – I just can’t help it!
17) It looks like Carlos _____(come) to the party tonight.
18) Right now I _____(spend) time with my sister.
19) Pedro _____(travel) to Madrid for work a lot.
20) Ssshhh! The baby _____(sleep).
Ejercicios
Completa con la forma correcta del present continuous.
Conjuga los verbos entre paréntesis en present continuous.
Formula oraciones interrogativas en present continuous.
Uso y ejercicios con Do y Does en inglés con explicación
Antes de comenzar el ejercicio recuerda que “do” y “does” son auxiliares para el presente simple. Lee la siguiente explicación:
Do: se utiliza para preguntas y respuestas con los pronombres we, I, you y they. Ejemplo:
- Do they play tennis? (¿Ellos juegan tenis?)
- Yes, they do. (Sí)
Uso y ejercicios con Do y Does en inglés con explicación
Antes de comenzar el ejercicio recuerda que “do” y “does” son auxiliares para el presente simple. Lee la siguiente explicación:
Do: se utiliza para preguntas y respuestas con los pronombres we, I, you y they. Ejemplo:
- Do they play tennis? (¿Ellos juegan tenis?)
- Yes, they do. (Sí)
Does: se utiliza para preguntas y respuestas con los pronombres he, she y it. Ejemplo:
- Does he study English? (¿Él estudia inglés?)
- Yes, he does. (Sí)
Finalmente, estos auxiliares no tienen un significado como tal; más bien son necesarios gramaticalmente.
“Do” también puede ser un verbo como en “I do homework” (Yo hago la tarea); sin embargo en este ejercicio va a ser utilizado siempre como auxiliar.
Completa las oraciones con “do” o “does”
1.
- she play soccer?
2.
- you like listening to music?
3.
- you watch TV at night? Yes, I .
4.
- Laura work on Saturdays? Yes, she .
5.
- the cat drink milk? Yes, it .
6.
- the cats drink milk? Yes, they .
7.
- Maria and Laura listen to music at home?
8.
- the computer work fine? Yes, it .
Ejercicios DO y DOES
En este test vamos a trabajar, no solo el DO y el DOES, sino que vamos a añadir también su forma del pasado: el DID. Conocer bien los tres es imprescindible para hacer preguntas, ya que TO DO, a parte de ser un verbo, también es un auxiliar de otros verbos. Así pues, en los ejercicios que tienes justo a continuación vas a poder comprobar tu dominio de estas partículas en inglés.
____ she want to come? (¿Quiere venir ella?)
He ____ play tennis (Él no juega a tenis)
I ____ love you! (¡Yo sí te quiero!)
____ you want to go to London? (¿No quieres ir a Londres?)
They ____ like pineapple (A ellos sí les gusta la piña)
Why ____ we fight for this? (¿Por qué luchamos por esto?)
____ she like pears? Yes, she ____ (Le gustan las peras? Sí, le gustan)
Anne speaks French, ____ she? (Anne habla francés, ¿no?)
You never cry, ____ you? (Tú nunca lloras, ¿verdad?)
It ____ hurt! (¡Sí que duele!)
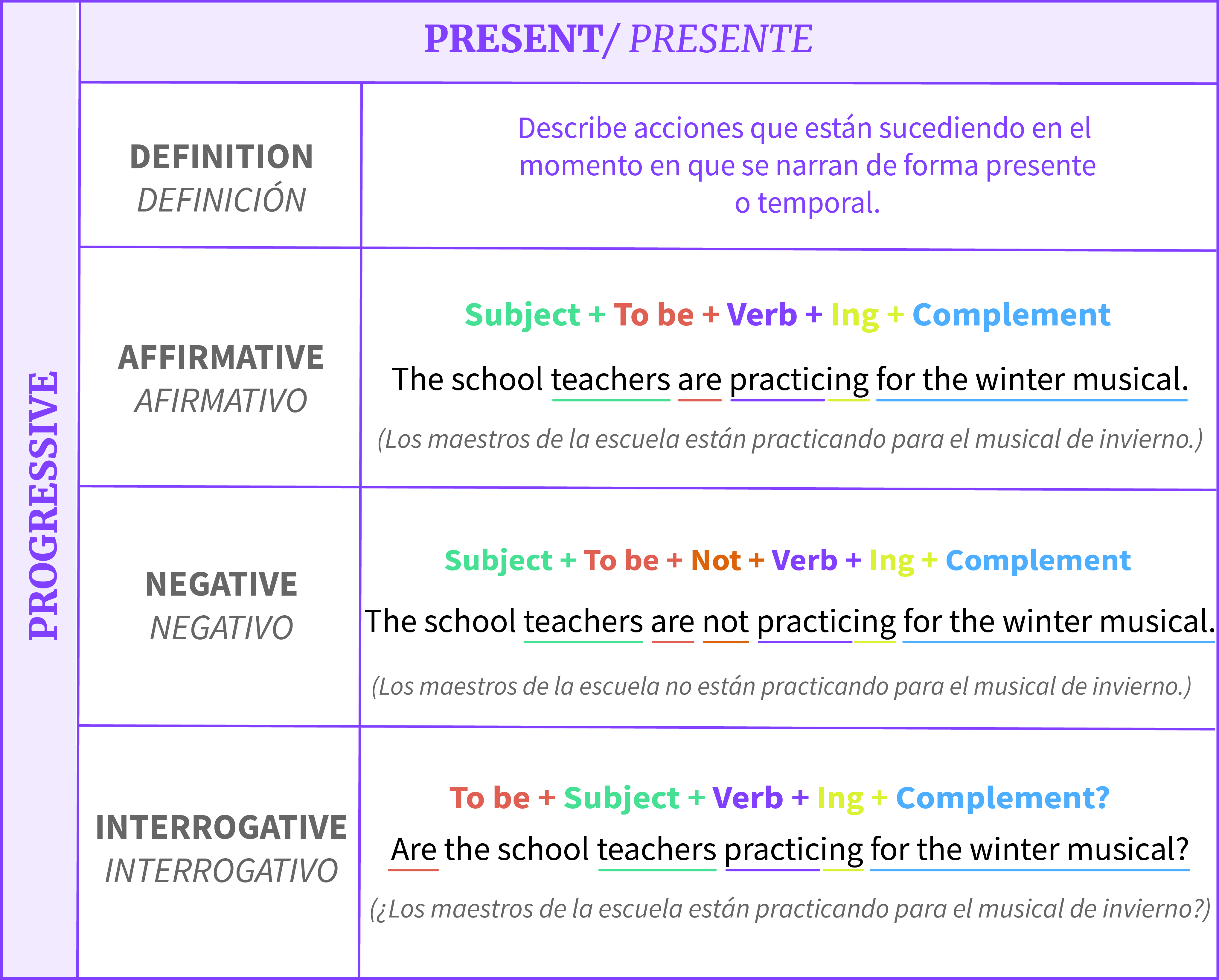
El present continuous o presente continuo es muy sencillo de entender y usar. Se forma igual que en castellano y se usa prácticamente en las mismas situaciones. Vamos a verlo con unos ejemplos y finalmente con un video explativo.
La teoría
¿Para qué se usa?
Para describir acciones que están ocurriendo en este momento, es decir, en el momento en el que se está hablando. También se puede usar para hablar del futuro, como explicamos en este otro artículo. De momento, vamos a centrarnos en el presente.
¿Cómo se forma?
Con el verbo to be en presente simple (am, is, are) más el verbo principal en gerundio (terminado en –ing). La regla de oro es que el 99 % de las veces que lo usamos, contraemos al hablar.
Afirmativa
Sujeto + am | is | are + verbo acabado en -ing
Esmérate muchísimo en aprender la forma contraída, tal y como la ponemos en estos ejemplos:
| I am learning English. | I’m learning English. |
| You are learning German. | You’re learning German. |
| She is learning Spanish. | She’s learning Spanish. |
Negativa
Sujeto + am not | isn't | aren't + verbo acabado en -ing
Ten en cuenta que también podemos contraer el verbo to be con el sujeto y, simplemente, añadir not detrás, como puedes ver en los ejemplos de abajo. Ambas son válidas, ¡lo importante es que lo contraigas!
| I am not learning English. | I’m not learning English. |
| We are not learning German. | We aren't learning German. | We're not learning German. |
| He is not learning Spanish. | He isn't learning Spanish | He’s not learning Spanish. |
Interrogativa
Am | is | are + sujeto + verbo acabado en -ing
Para hacer preguntas, lo único que tienes que hacer es invertir el orden del sujeto y del verbo to be. ¡Ah! Y aquí nada de contraer. Para contestar con short answers (respuestas cortas), solo tienes que poner el verbo to be en afirmativa o en negativa, detrás del sujeto. Fíjate en los ejemplos.
| Am I am learning English? | Yes, you are. |
| Are they learning German? | No, they aren't. |
| Is it working? | Yes, it is. |
La práctica
Empecemos practicando con la afirmativa. Antes, unas notas sobre pronunciación:
- Junta los labios al decir la m de I’m, /áim/
- Pronuncia bien la s de he’s, /hhhiis/ y she’s, /shhhiis/
- You’re, we’re y they’re suenan así: /ióo/, /uía/ y /dzéa/
| Estoy mirando el reloj de pared. | I’m looking at the clock. |
| Te estoy mirando. | I’m looking at you. |
| Estoy hablando con ellos. | I’m talking to them. |
| Estoy escuchando la radio. | I’m listening to the radio. |
| Ella está hablando con él. | She’s talking to him. |
| Él está escuchando las noticias. | He’s listening to the news. |
| Me estás leyendo un libro. | You’re reading a book to me. |
| Están soñando con la Navidad. | They’re dreaming about Christmas. |
| Estamos escribiendo al periódico. | We’re writing to the newspaper. |
Vamos ahora con negativa. Tienes que saber que...
- Isn't se pronuncia /isnt/
- Aren't suenan así: /aaant/, y no /árent/ ni nada parecido
| No estoy mirando a Laura. | I'm not looking at Laura. |
| No estoy cantando. | I’m not singing. |
| No estoy comiendo chocolate. | I’m not eating chocolate. |
| No estoy viendo la tele. | I’m not watching TV. |
| Ella no está saliendo con él. | She’s not dating him. | She isn't dating him. |
| Él no está escuchando música. | He’s not listening to the news. | He isn't listening to the news. |
| No estás leyendo un poema. | You’re not reading a poem. | You aren't reading a poem. |
| No están haciendo los deberes. | They’re not doing their homework. | They're doing their homework. |
| No estamos bebiendo cerveza. | We’re not drinking beer. | We aren't driniking beer. |
Y acabemos con la interrogativa. ¡Venga, que ya casi estamos! Fíjate en que aquí no hablamos de yes/no questions como en los ejemplos que vimos antes, sino de preguntas que requieren una frase completa como respuesta. Por eso empiezan con las partículas interrogativas what (qué), where (dónde), how (cómo), etc. ¡A practicar!
| ¿Qué estás haciendo ahora mismo? | What are you doing right now? |
| ¿De qué estoy hablando? | What am I talking about? |
| ¿Dónde está él trabajando ahora mismo? | Where’s he working right now? |
| ¿Cómo está gestionándolo ella? | How is she dealing with it? |
| ¿Qué estamos aprendiendo? | What are we learning? |
| ¿Adónde estáis yendo? | Where are you going? |
| ¿Cómo están haciéndolo ellos? | How're they doing it? |
| ¿Para qué hace ese ruido? | What’s it making that noise for? |
| ¿Para qué parpadea? | What’s it flashing for? |
Ejercicios con el verbo to be en inglés
- Jim ________ eating ice cream.
- The kids ________ playing in the park.
- Birds ________ singing.
- Henry and I ________ watching football.
- Bees ________ gathering honey.
- Tom and Karen ________ skiing.
- Sam ________ washing her hands.
- Tim ________ crying.
- They ________ rowing the boat.
- I ________ drinking wine.
- The birds ________ flying south.
- They ______ loving parents.
- I ________ dancing.
- Sarah and Thomas ________ getting married.
- I ________ beginning to understand English.
- The house ________ burning down.
- The fruit ________ hanging low on the tree.
- The baby ________ waking up.
- I ________ crawling.
- There ________ a meaning to every poem.
Ejercicios: presentsimple y continuous
Ahora, vamos a practicar un poco con estos ejercicios. Solo tienes que completar las frases propuestas con la forma adecuada de presente simple o continuo del verbo entre paréntesis. Encontrarás las soluciones más abajo pero recuerda, ¡no vale hacer trampas!
1) I _____ (work) for the Government.
2) The sun _____ (set) in the west.
3) The milk _____ (boil) already. Can you turn off the stove?
4) Peter is sick, so he _____ (not work) tomorrow.
5) I _____ to the radio in my way to work every morning.
6) I have a chronic condition, so I _____(take) a pill daily.
7) Who is that girl? Why _____ she _____ (dance) alone?
8) My mother _____ (say) she’s 55, but nobody _____ (believe) her.
9) Where _____ you _____(work)?
10) Listen! They are _____(play) that song you really like.
11) I have cabin fever, I really _____(want) to go outside.
12) My grandparents _____(love) each other so much -it’s very sweet!
13) I _____(stay) at this hostel during my next trip.
14) Please, stay quiet. I_____ (try) to work here!
15) My cousin _____(have) really long hair.
16) I often _____(sing) in the shower – I just can’t help it!
17) It looks like Carlos _____(come) to the party tonight.
18) Right now I _____(spend) time with my sister.
19) Pedro _____(travel) to Madrid for work a lot.
20) Ssshhh! The baby _____(sleep).
Ejercicios
Completa con la forma correcta del present continuous.
Conjuga los verbos entre paréntesis en present continuous.
Formula oraciones interrogativas en present continuous.
...
Form (Forma)
Ejercicios con el verbo to be en inglés
- Jim ________ eating ice cream.
- The kids ________ playing in the park.
- Birds ________ singing.
- Henry and I ________ watching football.
- Bees ________ gathering honey.
- Tom and Karen ________ skiing.
- Sam ________ washing her hands.
- Tim ________ crying.
- They ________ rowing the boat.
- I ________ drinking wine.
- The birds ________ flying south.
- They ______ loving parents.
- I ________ dancing.
- Sarah and Thomas ________ getting married.
- I ________ beginning to understand English.
- The house ________ burning down.
- The fruit ________ hanging low on the tree.
- The baby ________ waking up.
- I ________ crawling.
- There ________ a meaning to every poem.
Ejercicios con Presente Continuo: afirmaciones
- Tina ___________ ___________ water. (drink)
- They ___________ __________ to France. (travel)
- Fred ___________ ___________ a pie. (eat)
- The weather ___________ always ______. (change)
- She ___________ ___________ pasta. (cook)
- It ___________ __________ outside. (rain)
- The lady ___________ __________ for the bus. (wait)
- I ___________ __________ my aunt. (visit)
- It ___________ ___________ cold outside. (freeze).
- Jack and Jill ___________ _________ up the hill. (climb)
- Mom ___________ ___________ out to buy some groceries. (go)
- The little girl ___________ ___________ the newspaper. (tear)
- Nadal ___________ ___________ the match. (win)
- Janet ___________ ___________ tea. (have)
- The thief ___________ ___________ behind the bushes. (hide)
- The sun ___________ ___________ brightly. (shine)
- The birds ___________ ___________. (fly)
- Gina’s son ___________ ___________ his cat with a blanket. (cover)
- I ___________ ___________ a letter. (write)
- I ___________ __________ some eggs to make an omelette. (bea
| Ejemplos de nombres incontables | |
Bread Butter Coffee Money Love water Milk Work Soap Sugar Wood Time Meat Salt Paper Rice Honey Cheese | Pan Mantequilla Café Dinero Amor Agua Leche Trabajo Jabón Azúcar Madera Tiempo Carne Sal Papel Arroz Miel Queso |
Let's practice
Presente simple 'There is' y 'there are'
There are some books on the chair.
Adjetivos posesivos y pronombres posesivos
- Yours
- His
- I
- They
- It
- Yours
- Theirs
- Yours
- We
- Yours
- Me
- She
- Mine
- Hers
- It
- Its
- Their
- You
- Its
- Ours
- I
Adjetivos y pronombres posesivos - Ejercicios
| 1) | These are books. | Estos son vuestros libros |
| 2) | The car is . | El coche es mío |
| 3) | The dog is . | El perro es tuyo |
| 4) | These are glasses | Estas son mis gafas |
| 5) | I am waiter. | Yo soy vuestro camarero |
| 6) | Is brother here? | ¿Está mi hermano aquí? |
| 7) | The book is . | El libro es nuestro |
| 8) | car is there. | Su (de ellos) está allí |
| 9) | This is house. | Esta es su casa (de ella) |
| 10) | friend is waiting. | Tu amigo está esperando |
| 11) | pencils are green. | Vuestros lápices son verdes |
| 12) | parents are at home. | Mis padres están en casa |
| 13) | The dog likes food. | Al perro le gusta su comida |
| 14) | The restaurant is . | El restaurante es nuestro |
| 15) | Where are shoes? | ¿Dónde están tus zapatos? |
| 16) | phone number is... | Mi número de teléfono es... |
| 17) | leash is in my car. | Su correa (de perro) está en mi coche |
| 18) | This is . | Esto es suyo (de ellos) |
| 19) | This is sandwich. | Este es su (de ella) sandwich |
| 20) | tea is too hot. | Mi té está demasiado caliente |
mine (máin) - (el/la/lo/los/las) mío/a míos/as
- Can you lend me a pencil? - I forgot mine.
¿Puedes prestarme un lápiz? - Olvidé el mío. - Here are your tools. Where are mine?
Aquí están tus herramientas. ¿Dónde están las mías? - This belongs to me. It's mine.
Esto me pertenece. Es mío. - I play tennis with a friend of mine.
Juego al tenis con un amigo mío (de los míos).
yours (iórs) - (el/la/lo/los/las) tuyo/a tuyos/as
- Is this book yours?
¿Es tuyo este libro? - That is my problem, not yours.
Ese es mi problema, no tuyo. - This belongs to you. It's yours.
Esto te pertenece. Es tuyo. - I met a friend of yours yesterday.
Conocí a un amigo tuyo (de los tuyos) ayer.
his (jis) - (el/la/lo/los/las) suyo/a suyos/as
- I lent Bob my car and he lent me his.
Le presté a Bob mi auto y él me prestó el suyo. - Jack wears a nice hat. Is it his?
Jack usa un lindo sombrero.¿Es suyo (de él)? - This belongs to John. It's his.
Esto pertenece a John. Es de él. - Bill went to the game with a friend of his.
Bill fue al juego con un amigo de él (de los de él).
hers (jers) - (el/la/lo/los/las) suyo/a suyos/as
- I forgot my book, so Susan gave me hers.
Olvidé mi libro, entonces Susan me dió el suyo. - That is not my sister's car. Hers is red.
Ese no es el auto de mi hermana. El de ella es rojo. - This belongs to Sally. It's hers.
Esto pertenece a Sally. Es de ella. - Mary went to the theater with a friend of hers.
Mary fue al teatro con una amiga de ella.
ours (áurs) - (el/la/lo/los/las) nuestro/a, nuestros/as
- Their city is old. Ours is new.
Su ciudad es vieja. La nuestra es nueva. - Their country is bigger than ours.
Su país es más grande que el nuestro. - It's their problem, not ours.
Es su problema, no el nuestro. - Sally and I had a big party with some friends of ours.
Sally y yo tuvimos una gran fiesta con algunos amigos nuestros.
yours (iórs) - (el/la/lo/los/las) de ustedes
- Our language is nice. Yours is practical.
Nuestro idioma es lindo. El de ustedes es práctico. - Our house is next to yours.
Nuestra casa está al lado de la de ustedes. - This belongs to you and your brother. It's yours.
Esto pertenece a ti y a tu hermano. Es de ustedes. - You can bring some friends of yours, if you want.
Ustedes pueden traer algunos amigos suyos si quieren.
theirs (dérs) - (el/la/lo/los/las) suyo/a suyos/as
- That car belongs to my parents. It's theirs.
Ese coche pertenece a mis padres. Es de ellos. - Our city is as nice as theirs.
Nuestra ciudad es tan linda como la de ellos. - My appartment is here. Theirs is there.
Mi apartamento está aquí. El de ellos está allí. - My parents went on vacation with friends of theirs.
Mis padres se fueron de vacaciones con amigos suyos.
- The phone number you call last night is ______ .
- Mine
- He
- You
- Yours
- His
- I
- They
- It
- Yours
- Theirs
- Yours
- We
- Yours
- Me
- She
- Mine
- Hers
- It
- Its
- Their
- You
- Its
- Ours
- I
- My – mi.
- Your (singular) – tu, su.
- His – su (de él)
- Her – su (de ella)
- Its – su (de eso)
- Our – nuestro/a.
- Your (plural) – su (también vuestro/a para los Españoles)
- Their – su (de ellos/ellas)
- Primera persona singular: my. I brush my teeth every day.
- Segunda persona singular: your. Your new shirt is very beautiful. Recuerda que en inglés no distinguimos entre informal (tú) y formal (usted).
- Tercera persona singular: his / her / its. Her brother goes to the new gym. Aquí es donde vienen muchos dolores de cabeza para los españoles, ya que tendemos a confundirlos. Recuerda que his se usa cuando el poseedor es un hombre, her cuando es mujer e its cuando es una cosa (o en algunos casos, para animales).
- Primera persona plural: our. Our town is far away from the coast.
- Segunda persona plural: your. Your names are Peter and Sandy. Además de ser igual que el singular, tampoco distingue entre formal e informal.
- Tercera persona plural: their. Their English teacher seems very nice.
- Al igual que ocurre con los adjetivos en general (como new o tall, por ejemplo), los adjetivos posesivos no tienen plural en inglés. Esto es, que no cambiamos el adjetivo posesivo dependiendo de si va con un nombre en singular o en plural: my book / my books.
- Recuerda que los adjetivos posesivos van siempre delante del sustantivo, ¡o parecerás Yoda! Por ejemplo, my car is red, nunca
car my is red
Vamos a hacer unos ejercicios
Escoge el adjetivo posesivo adecuado según se necesite en cada frase:
- I love my sister. _____ name is Sandra.
- I live in Barcelona. However, ______ friends live in Madrid.
- Anna and Katie like dogs. _______ parents like dogs too.
- I have a brother. _____ name is Tom.
- Me and my friends rent a flat. _____ flat is beautiful
- Escribe el adjetivo posesivo (my, your, his, her, its, our, their) de forma correcta:1.
- I love my mother. name is Marina.
- 2.
- I am Charles. last name is Smith.
- 3.
- I love my mother and my father. names are Charles and Laura.
- 4.
- I have a brother. name is Allan.
- 5.
- I have a cat. name is Punchy.
- 6.
- You are Mark Smith. What is favorite movie, Mark?
- 7.
- My sister and I have a dog. dog is beautiful
| Pronombres Personales | Pronombres Acusativos | Adjetivos Posesivos | Pronombres Posesivos | Pronombres Reflexivos |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | me | my | mine | myself |
| you | you | your | yours | yourself |
| he | him | his | his | himself |
| she | her | her | hers | herself |
| it | it | its | -- | itself |
| we | us | our | ours | ourselves |
| you | you | your | yours | yourselves |
| they | them | their | theirs | themselves |
| Pronombres Indefinidos | ||||
| everybody | nobody | somebody | anybody | |
| everyone | no one | someone | anyone | |
| everything | nothing | something | anything | |
| Pronombres Relativos | ||||
| who | which | that | whom | whose |
| Pronombres Recíprocos | ||||
| each other / one another | ||||
PRESENTE CONTINUO
Escribe los verbos de las siguientes oraciones en presente continuo.
1 My sisters (go)
home now.
2 We (do)
our homework.
3 She (play)
games on the computer.
4 People (wait)
for the concert to start.
5 My grandfather (sleep)
now.
6 You (drive)
the car too fast.
7 She (work)
hard to get the job.
8 She (have)
a bath at the moment.
9 That old woman (visit)
the doctor tomorrow.
10 Look at the window. It (snow)
FORMAS AFIRMATIVAS, NEGATIVAS E INTERROGATIVAS
Afirmación Negación Interrogación I am eating I´m not eating Am I eating? You are eating You aren´t eating Are you eating? He / she is eating He / she isn´t eating Is he/she eating? We are eating We aren’t eating Are we eating? You are eating You aren’t eating Are you eating? They are eating They aren’t eating Are they eating?
Ejercicios del presente continuo interrogativo
| Afirmación | Negación | Interrogación |
| I am eating | I´m not eating | Am I eating? |
| You are eating | You aren´t eating | Are you eating? |
| He / she is eating | He / she isn´t eating | Is he/she eating? |
| We are eating | We aren’t eating | Are we eating? |
| You are eating | You aren’t eating | Are you eating? |
| They are eating | They aren’t eating | Are they eating? |
Ejercicios del presente continuo interrogativo
- They are writing letters. ? ...
- She is having lunch. Where. ...
- She's not having a good time. Why. ...
- The boy is playing football. Where. ...
- She is going on holiday. ...
- Your family is staying with... ...
- Peter is talking on the phone. ...
- Tom and his company are doing business abroad.
- They are writing letters. ? ...
- She is having lunch. Where. ...
- She's not having a good time. Why. ...
- The boy is playing football. Where. ...
- She is going on holiday. ...
- Your family is staying with... ...
- Peter is talking on the phone. ...
- Tom and his company are doing business abroad.
La forma verbo + ing se llama participio de presente (gerundio).
¿Cómo se forma el participio de presente? Basta con añadir “ing” al verbo.
- Talk = talking.
- Mix = mixing.
- Play = playing.
Si el verbo acaba en consonante + vocal acentuada + consonante, debemos duplicar la consonante final antes de añadir el sufijo “ing”.
- Stop = stopping.
- Run = runnig.
- Begin = beginning.
Los verbos que acaban en vocal + consonante + “e” muda pierden la “e” final antes de añadir el sufijo “ing”.
- Dance = dancing.
- Bake = baking.
- Close = closing.
Pero, los verbos que acaban en doble “e” la mantienen antes de añadir el sufijo “ing”.
- Agree = agreeing.
Finalmente, hay algunos verbos en inglés que acaban en ie. Estos verbos cambian la ie por y antes de añadir el sufijo ing:
- Lie = lying.
- Tie = tying.
- Die = dying.
Complete the sentences using the present continuous:
1. I (write) a poem now.
2. She (leave) tomorrow morning.
3. We (build) a house.
4. Paul and Jennifer (study) French at university.
5. Peter (leave) outside.
6. Tom (teach) English at that high school.
7. You (make) a great effort.
8. They (tell) Mary what happened yesterday.
9. I (watch) TV right now.
10. She (play) volleyball this afternoon.
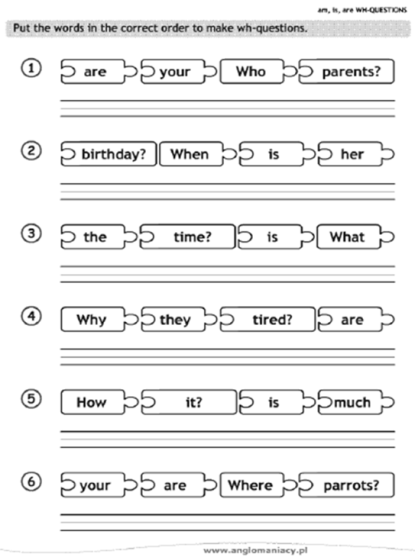
WH- Questions words: who, what, where, when, why
Wh- questions
- ____ colour are your eyes ?
- Where
- Who
- When
- What
Espere unos segundos para que se carguen las preguntas.
-
____ son mis llaves ?
- OMS
- Cuando
- Dónde
- Qué
- ____ son mis llaves ?
- OMS
- Cuando
- Dónde
- Qué
- ____ ¿visitas a tu familia?
Los domingos.- Cuales
- Dónde
- Cuando
- OMS
- ____ es el rey de españa?
Felipe VI- OMS
- Cuando
- Dónde
- Qué
- ____ años tiene tu hermana?
- OMS
- Cuales
- Cómo
- Cuando
- ____ uno te dieron?
El negro.- Por qué
- OMS
- Qué
- Cuales
- ____ ¿estás enojado conmigo hoy?
- OMS
- Cuando
- Dónde
- Por qué
- ____ ¿esa mujer está allá?
Esa es carol- OMS
- Por qué
- Cómo
- Cuando



No hay comentarios.:
Publicar un comentario